19 March 2021: Original Paper
Klotho Regulates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition In Vitro via Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Attenuates Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in a Rat Renal Transplant Model
Xiao-Jun Li 12ABEF* , Pei Lu 3BCDEF* , Xue-Feng Shao 2BDF , Ting Jiang 2CD , Feng Liu 2CD , Gang Li 1EFG*DOI: 10.12659/AOT.930066
Ann Transplant 2021; 26:e930066
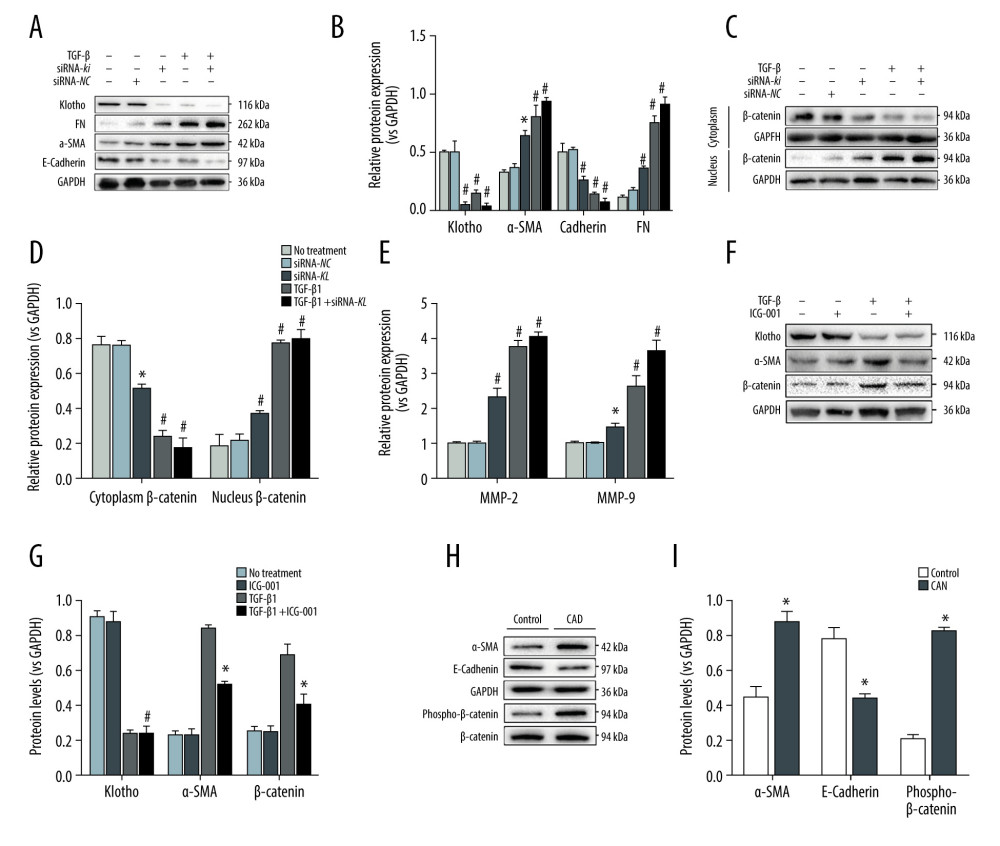
Figure 3 Loss of Klotho promoted the development of EMT and CAD by inhibiting activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. To confirm the role of loss of Klotho in the development of EMT and CAD, we transfected the HK-2 cells with siRNA-kl to silence the expression of Klotho and observed that the FN protein expression was remarkably increased after the inhibition of Klotho, along with the increase of EMT procedure in HK-2 cells (A, B). Furthermore, the contradictory expression of β-catenin in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HK2 cells was observed to be induced by the treatment of siRNA-kl (C, D). Combined with the increase of Wnt target gene – Matrix Metalloprotease-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9, activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by the loss of Klotho was examined (E). HK2 cells were treated with ICG-001, the specific inhibitor of β-catenin, and no change of expression of Klotho was found, along with the significant decrease of α-SMA (F, G). Finally, the effect of EMT and activation of β-catenin were tested in the rat CAD model, which was consistent with the in vitro results (H, I). * P<0.001 compared with control group; # P<0.0001 compared to control group. Each experiment was performed at least 3 times.


