31 March 2023: Original Paper
Evaluation and Use of Organs from Donors Poisoned by Organophosphorus Pesticide
Ji-hua Wu1AF, Xi-hua Ma1BCD, Jian-hui Dong1EF, Ning Wen1CD, Ke Qin1BCD, Liu-gen Lan1EF, Ji-xiang Liao1B, Zhi-ying Lei2CDF, Hai-bin Li1AE, Xu-yong Sun1AFG*DOI: 10.12659/AOT.939343
Ann Transplant 2023; 28:e939343
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to explore the evaluation and use of donor organs from donors with brain death caused by acute severe organophosphorus pesticides and provide a basis for the use of such donor organs.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Seven cases of brain dead donors caused by acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning from January 2014 to December 2018 in the hospital were collected, and a retrospective analysis was made of the donors’ age, race, physiological and pathological changes, donor organ function changes and the organ use, liver or kidney function recovery, and complications of the recipients. The 18 recipients were followed up until June 31, 2022.
RESULTS: We found that 71.42% of organ donors were male, and 71.42% of organ donors were under 50 years old. The main cause of death was respiratory failure caused by organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. The liver and kidney functions of 7 donors were damaged, and 3 livers could not be used due to severe functional damage, but the liver or kidney function of 18 recipients gradually recovered after transplantation. Delayed recovery of graft function occurred after transplantation accounted for 21.43%, and the grafts had good short-term to medium-term performance.
CONCLUSIONS: Although the function of organs from donor with brain death due to acute severe organophosphorus pesticide poisoning is seriously damaged, most of the organs can still be used for transplantation. Individualized functional maintenance according to the situation of donors is conducive to improving the quality of organs.
Keywords: Brain Death, Organ Transplantation, organophosphate poisoning, Tissue and Organ Procurement, Humans, Male, Middle Aged, Female, Organophosphorus Compounds, Liver Transplantation, Pesticides, Poisons, Tissue Donors, Graft Survival
Background
Although organ donation after the death has become the main source of organ transplantation in China, organ shortage is still one of the bottlenecks restricting the development of organ transplantation. To increase sources of organs, under strict evaluation and maintenance, it is important to seek a wider source of organs, striving to expand the application scope of donor organs, and expanding the use of marginal donors [1,2]. Organophosphorus (OPS) pesticide is widely used in China. OPS can enter the human body through many ways, such as skin, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, eyes, and wounds, easily causing acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning (AOPP). Every year, about 110 000 people worldwide die from AOPP, and countries in Southeast Asia, China, and Africa have the most cases [3]. The incidence of AOPP due to accidental ingestion or attempted suicide is highest in China [4]. There are few reports in China and elsewhere on the use of donors who are brain dead due to AOPP. Experience using such donor organs is relatively lacking. Therefore, our transplantation center carried out a retrospective analysis of the evaluation, maintenance, and use of organs from 7 donors who had brain death due to AOPP, and summarized the feasibility and safety of the use of the donor organs.
Material and Methods
COLLECTION OF DONOR DATA:
We collected relevant data of donor organs before and after acquisition, including age, sex, nationality, cause of death, duration of critical care, use of vasopressor drugs, and pathogen detection results, and we evaluated liver function by total bilirubin (STB), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), albumin (ALB), and prothrombin time (PT). We also assessed renal function by creatinine (Cr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), cold and hot ischemia time, and other risk factors of donor organs, as well as use of vasoactive drugs and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
COLLECTION OF RECIPIENT DATA AND FOLLOW-UP DATA:
The recipients’ data include age, sex, and primary liver or kidney disease. The follow-up data after transplantation included postoperative complications, recipient/graft survival time, and graft function.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
SPSS (23.0) statistical software was used to process the data. Count data were expressed as frequency and percentage, and measurement data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. Statistical analysis and comparison were conducted by
Results
GENERAL INFORMATION OF THE DONORS:
Two donors with AOPP were from tertiary hospitals and 5 were from secondary hospitals. Organ donation after the death of Chinese citizens can be divided into 3 categories: C-I, such as donation after brain death (DBD); C-II, such as donation after cardiac death (DCD); and C-III, such as donation after brain death awaiting cardiac death (DBCD) [6]. Among the donation cases, there were 5 C-I cases and 2 C-III cases. There were 5 male donors and 2 female donors. The donors’ average age was (23.75±15.39) years. Donor blood type was A in 3 cases, B in 2 cases, and O in 2 cases (Table 1).
DONOR-RELATED INFORMATION:
The results of pathogen testing were negative in all 7 donors. Six donors used vasopressor drugs. Five donors received cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR); among them, 2 donors used ECMO combined with CRRT for organ function maintenance and repair. The mean systolic blood pressure before organ extraction of the 7 donors was 101.57±22.50 mmHg. warm ischemia time (WIT) was less than 12 min in 85.71% of the donors, and 71.43% of organs had cold ischemia time (CIT) less than 12 h (Table 2).
DONOR ORGAN FUNCTION AND PATHOLOGY BEFORE DONATION:
All 7 donors had severe liver and kidney function damage before donation, and the liver function was mainly increased by transaminase and indirect bilirubin. Among them, 2 cases had severe acute liver function damage and 1 case was positive for hepatitis B and the liver was not obtained (Table 3). Kidney pathology showed epithelial cells in renal tubules had edema and microvilli shedding only (Figure 1). Liver pathology showed hepatocytes with slight edema, slight gallbladder silt, small infiltration of inflammatory cells, and occasional punctate necrosis (Figure 2).
APPLICATION OF EXTRACORPOREAL MEMBRANE OXYGENATION (ECMO) OF DONORS:
Two donors suffered from organ function damage due to extremely unstable hemodynamics and were treated with ECMO combined with continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). After ECMO treatment, AST and ALT of patients showed a downward trend, and BUN and Cr of renal function remained stable (Table 4).
RELEVANT DATA OF KIDNEY IN VITRO PERFUSION (LIFEPORT) IN ORGAN DONOR MAINTENANCE:
LifePort can judge the quality of kidney in general by circulating parameters during in vitro hypothermic perfusion, which has the advantages of rapid and dynamic observation, and plays an irreplaceable role in judging the quality of donor kidney and the results of transplantation [7]. LifePort can provide perfusion pressure, machine perfusion flow (MPF), resistance index (RI) and perfusion time. In this study, 8 donor kidneys were perfused in vitro (Table 5).
GENERAL INFORMATION OF RENAL TRANSPLANT RECIPIENTS: There were 14 recipients of kidney transplantation from donors poisoned by organophosphorus pesticides, including 13 males and 1 female, with an average age of 38.43±10.28 years. All 14 patients had hypertension before surgery and 78.57% of the primary disease was chronic glomerulonephritis. The average hospitalization time of the 14 recipients was 18.29±8.38 days. One of the recipients had urinary tract infection on the third day after the operation, and severe pneumonia occurred twice at 4 months and 10 months after the operation; the patient died of severe pneumonia at 10 months after the operation. Delayed recovery of graft function (DGF) occurred in 3 recipients, and regular hemodialysis treatment was carried out for 3 times/week for them. The recipients with DGF recovered well between 1 and 4 weeks after surgery (Table 6, Figure 3).
All 4 recipients of liver transplantation were adult males, aged 29–40 years old. All of them suffered from posthepatitic cirrhosis before the operation. The average hospitalization time was 27.75±3.30 days. There was 1 case of pulmonary infection after liver transplantation without other complications (Table 7).
RENAL FUNCTION RECOVERY OF RENAL TRANSPLANT RECIPIENTS:
The average preoperative serum creatinine Scr of 14 renal transplant recipients was 991.21±289.56 μmol/L, which began to decrease after the operation. Compared with preoperative Scr, there was a statistically significant difference on the 7th day (
LIVER FUNCTION AFTER LIVER TRANSPLANTATION: The graft liver function was gradually recovered. Bilirubin, ALT, AST, and PT decreased slowly, albumin increased slowly, and liver function recovered gradually after the operation (Table 8).
FOLLOW-UP OF RECIPIENT/GRAFT SURVIVAL AFTER LIVER AND KIDNEY TRANSPLANTATION: All recipients were followed up regularly after discharge to understand the graft liver/kidney function. As of June 2022, the follow-up time of all recipients was 4–8 years. All 14 patients received successful renal transplantation, with a survival rate of 100% at 28 days after the operation. One patient died of severe pneumonia 10 months after the operation. The 1-year survival rate of the 14 renal transplant patients was 92.86%. The recipient/graft survival of transplanted livers and kidneys was good (Figure 4).
Discussion
The annual output of organic phosphorus in China accounts for 33.0~35.0% of the world’s total [3]. AOPP accounts for 20~50% of toxic cases, and the case-fatality rate is 3~40%. It is characterized by acute onset, rapid progression, and high mortality [8]. However, use of AOPP donors has rarely been reported worldwide or in China, which is mainly concerned about organ damage caused by toxicity and poor long-term prognosis. Organophosphorus pesticides are mainly metabolized by the liver, and metabolites are mainly excreted in urine through the kidney. The extent of organ damage caused by organophosphorus pesticides is related to the distribution of cholinergic nerves and the tolerance of the organs to cholinergic crises. Therefore, the target organs directly affected by organophosphorus pesticides are mainly the heart, brain, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract, and there is no direct organic damage to the liver and kidney. It can be confirmed from our renal puncture and liver puncture pathological examination (Figures 1, 2). Although the donors are mainly young and middle-aged (Table 1), the data show that the liver and kidney functions of the donors are moderately damaged (Table 3), and the liver damaged is mainly shown by the increase of transaminase and indirect bilirubin. The main reason is that in addition to the direct toxic effect of drugs, AOPP is often accompanied by systemic inflammatory response syndrome, which can activate immune cells to release a large number of inflammatory mediators and cytokines, forming a cascade reaction and causing apoptosis. It also increases vascular permeability and activates the coagulation fibrinolysis system, leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), aggravating microcirculation disorders and leading to organ damage [9,10]. In addition, after the brain death of patients with organophosphorus poisoning, a large number of catecholamines are released and exhausted, and the lack of antidiuretic hormone leads to diabetes insipidus, leading to unstable hemodynamics, which easily leads to insufficient tissue perfusion and oxygen supply (Table 2), which is also an important cause of organ function damage.
Among the 7 donors, 3 needed cardiopulmonary resuscitation due to hemodynamic instability, resulting in liver and kidney function damage. Among them, 2 patients were given ECMO for hemodynamic stability support, which can greatly improve organ function (Table 4). ECMO can quickly repair liver function, which proves that organophosphorus pesticide poisoning does not directly cause liver and kidney function damage. We performed in vitro hypothermic perfusion (HMP) on 8 donor kidneys. HMP played an important role in evaluating and improving the quality of donor kidneys and reducing the DGF of the transplanted kidneys (Table 5). It is widely used in the era of organ donor kidney transplantation after brain death. We used the LifePort mechanical perfusion to assess donor kidney flow and resistance. In addition, RI and MPF were used to evaluate renal quality [11]: RI <0.3, MPF >100 mL/min, the renal quality was good; RI <0.4, MPF >80 mL/min, which can be used for transplantation; RI 0.4~0.6, MPF 50~80 mL/min, combined with clinical data to judge the quality of donor kidney to determine whether to transplant; RI>0.6, MPF<50 mL/min, it is recommended to discard. In this study, we collected data on flow and resistance of 8 donor kidneys. Combined with the clinical data of donors and the pathological examination of donor kidneys, it was judged that kidneys could be used for transplantation. Among the 7 donor livers, 3 had severe liver function damage, mainly due to the increase of enzyme spectrum and bilirubin. Considering that the main cause was related to ischemia and hypoxia injury, and there was no evidence of direct injury caused by pesticide poisoning, 3 donor livers were abandoned after comprehensive evaluation. The remaining 4 livers were used for transplantation after pathological biopsy evaluation (Figures 2). The effect was good, without graft-related complications, and the patient/graft survival rate was good.
Among the 14 renal transplant recipients, DGF occurred in 3 cases after surgery. DGF had an impact on the long-term survival of patients/grafts [12]. Three patients were given regular hemodialysis transitional treatment. Creatinine in all patients recovered to normal within 1 month after surgery, and the function of transplanted kidneys recovered well. This kind of donor organ can achieve good results after evaluation and organ function repair. Among the 14 recipients, 1 patient developed urinary tract infection in the perioperative period and developed severe pneumonia 10 months after the operation; this patient died of severe infection. Postoperative pulmonary infection was mainly related to a variety of factors, such as prophylactic use of antibiotics before the operation, pathogen culture of perfusion fluid, postoperative medication, and postoperative lifestyle. At present, there is no direct evidence of lethal acute organophosphorus poisoning. None of the patients had any clinical manifestations of organophosphorus pesticide poisoning, and there were no complications such as bleeding, embolism, vascular stenosis, ureteral obstruction, and acute rejection (Table 6). This shows that there is no toxin residue in the liver and kidney of the donor after organophosphorus pesticide poisoning, which will affect the recipients, and will not increase the incidence of complications. The use of these donors ensures the safety of the recipients. The mean value of Scr in the 14 recipients showed a downward trend after surgery, and compared with that before surgery, the function of transplanted kidney began to recover gradually on the 7th day after surgery (Figure 3). We monitored the liver function of the recipients after liver transplantation, and the liver function of 4 patients improved gradually after liver transplantation, indicating that there was no significant impact on the donor liver function postoperative (Table 8). We followed up the patients after liver transplantation and found that there were no infection or other complications (Table 7). One year after the operation, 4 patients/grafts survived and the liver function was normal. The liver and kidney functions of these donors were not affected after surgery. However, because it is easy to cause serious hemodynamic fluctuations, such donors should be intervened as soon as possible to protect and repair the function of donor organs by taking measures such as rapidly removing toxins, limiting the absorption of toxins, use of anticholinergic drugs and cholinesterase reactivators, blood purification therapy, respirators, and ECMO to remove inflammatory agents, and ensuring tissue perfusion and oxygenation. Long-term follow-up showed that such donors had no significant impact on patient/graft survival (Figure 4).The follow-up data shows the availability and safety of AOPP donor organs.
Conclusions
Acute severe organophosphorus pesticide poisoning usually leads to multiple organ function damage of brain dead donors, mainly due to the tissue damage caused by insufficient blood supply, oxygen supply, and inflammatory response syndrome caused by the donors’ circulatory and respiratory dysfunction, which is not the direct toxic effect of drugs. By taking effective intervention measures, it is conducive to the protection and repair of various organ functions. Through strict comprehensive evaluation, both livers and kidneys of AOPP donors can be used for transplantation. The organ function recovers well after surgery, and good long-term results have been achieved. Therefore, brain dead donors from AOPP can be used as a safe source of organ transplantation donors.
Figures
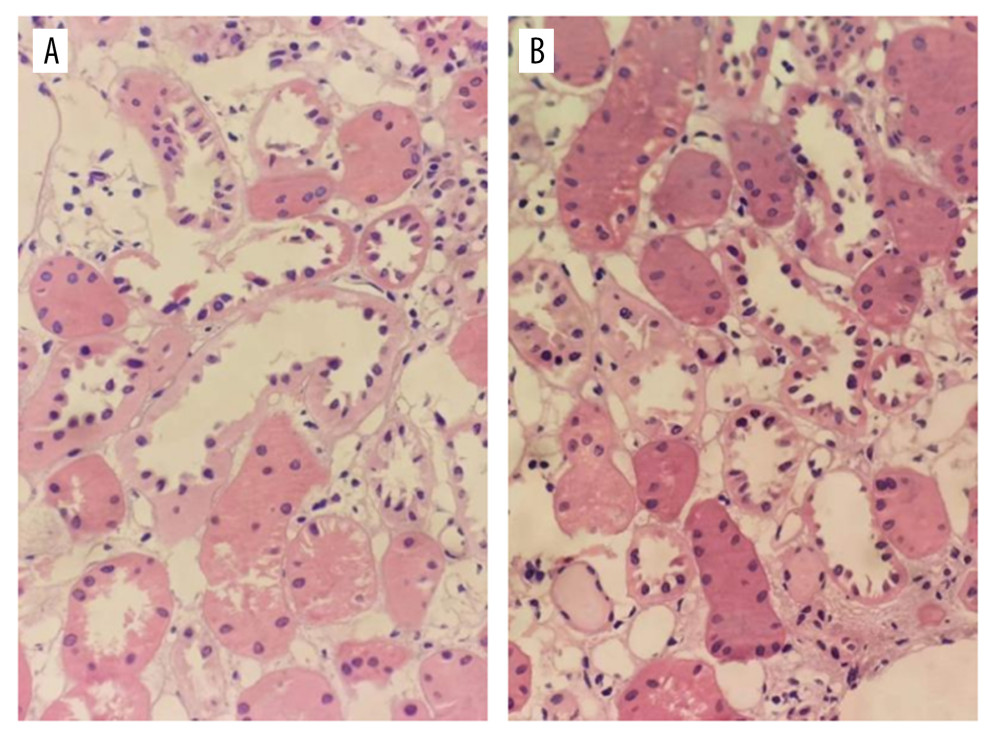 Figure 1. Pathological examination of donor kidney zero-point puncture biopsy. Figures A and B show the tubular type of epithelial cells in renal tubules. Some epithelial cells in renal tubules show edema with microvilli shedding (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×).
Figure 1. Pathological examination of donor kidney zero-point puncture biopsy. Figures A and B show the tubular type of epithelial cells in renal tubules. Some epithelial cells in renal tubules show edema with microvilli shedding (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×). 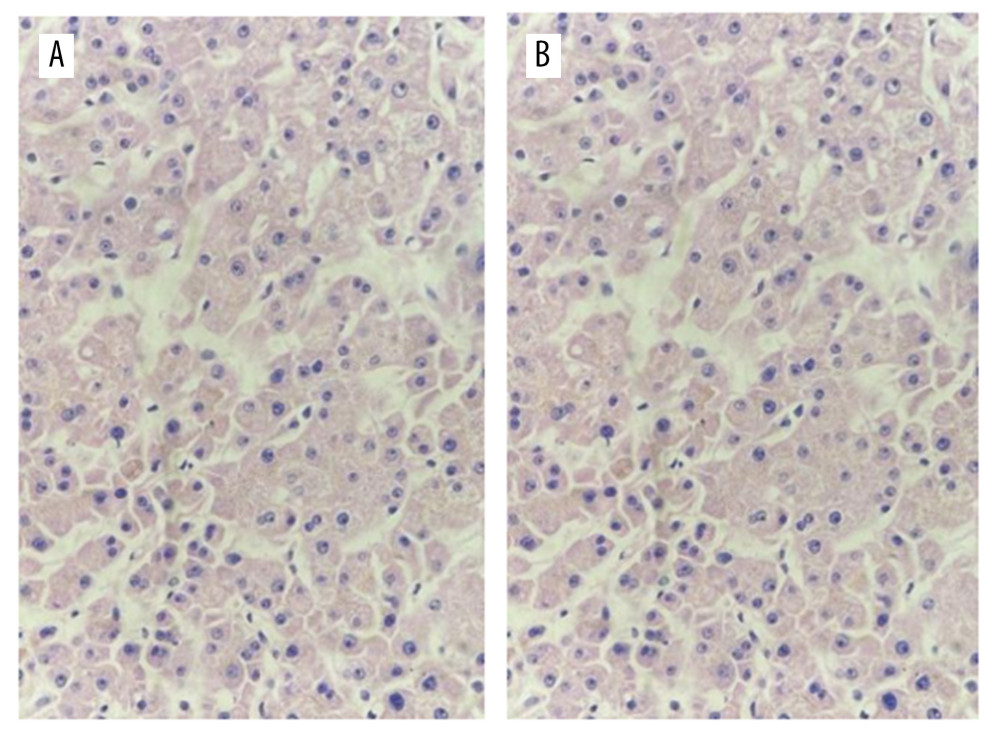 Figure 2. Liver zero-point puncture for pathological examination. Figures A and B show hepatocytes with slight edema, slight gallbladder silt, small infiltration of inflammatory cells, and occasionally punctate necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×).
Figure 2. Liver zero-point puncture for pathological examination. Figures A and B show hepatocytes with slight edema, slight gallbladder silt, small infiltration of inflammatory cells, and occasionally punctate necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×). 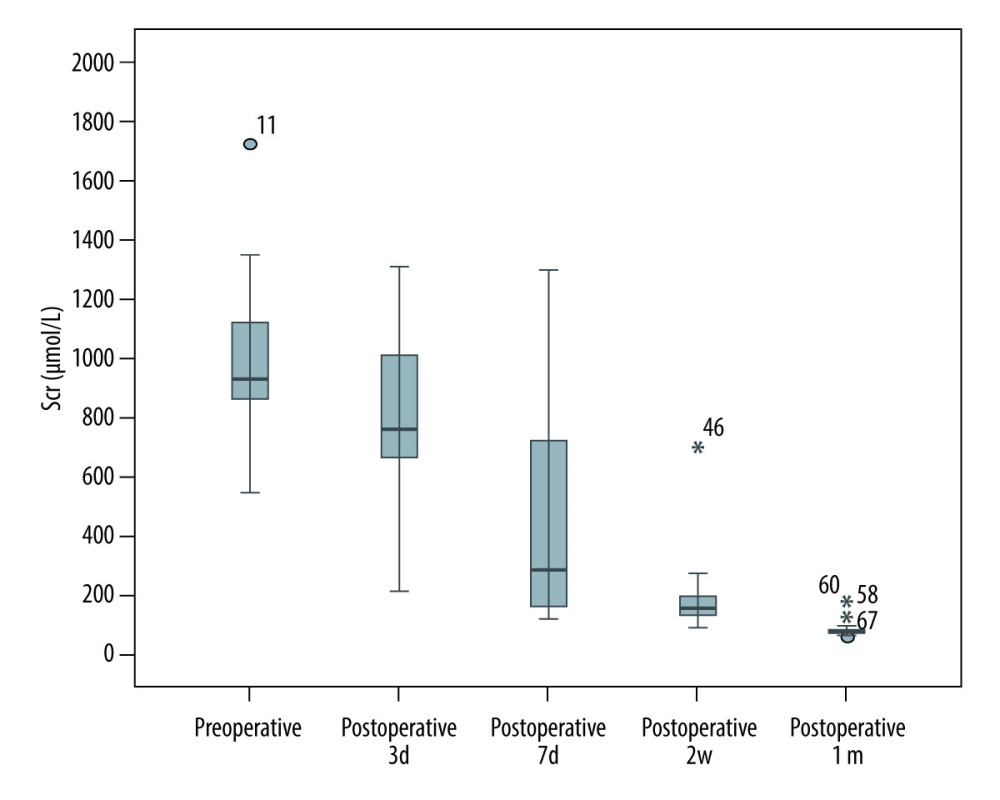 Figure 3. Comparison of creatinine before and after renal transplantation in 14 recipients.
Figure 3. Comparison of creatinine before and after renal transplantation in 14 recipients. 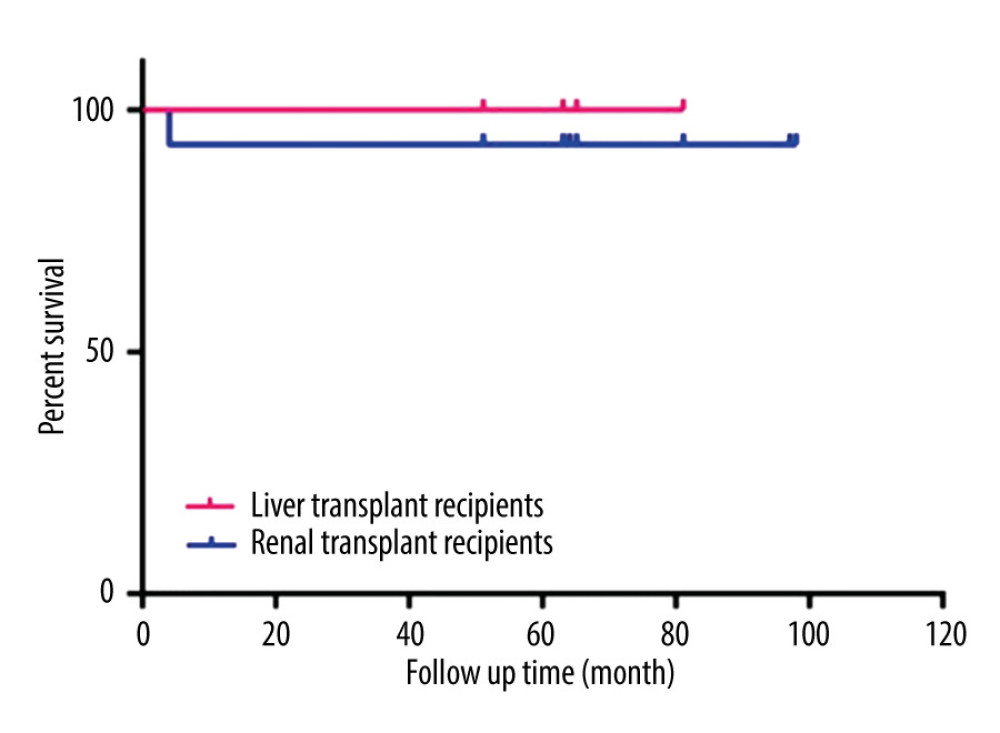 Figure 4. Follow-up recipients/graft survival in liver transplant and kidney transplant.
Figure 4. Follow-up recipients/graft survival in liver transplant and kidney transplant. Tables
Table 1. General information of donors.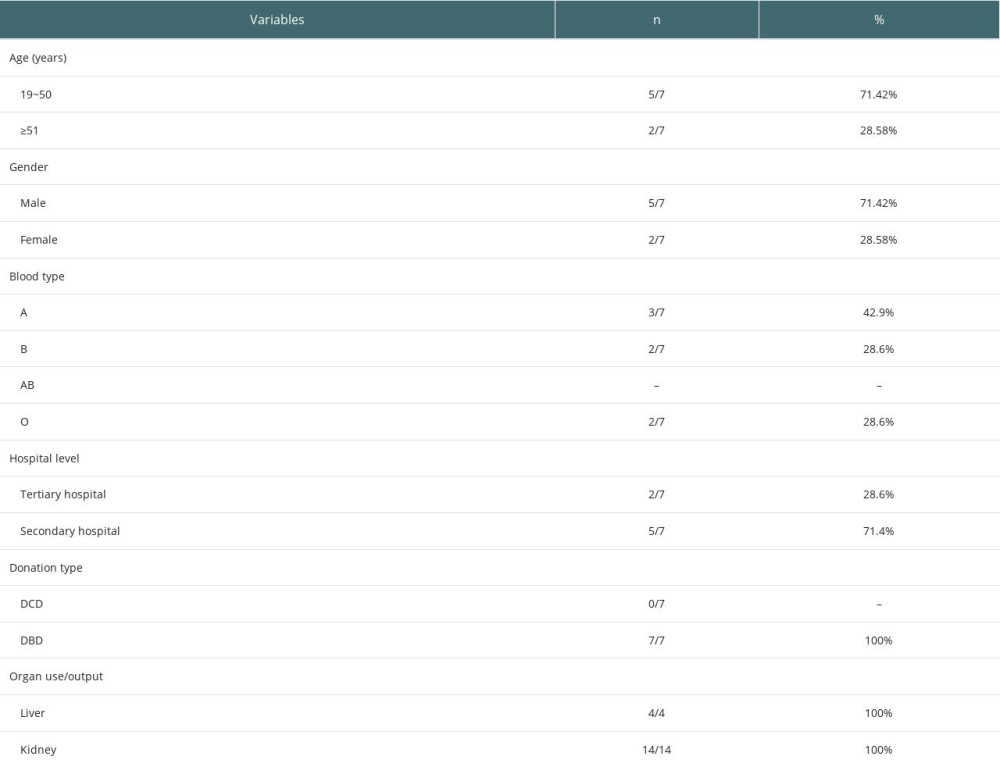 Table 2. Donor clinical parameters.
Table 2. Donor clinical parameters.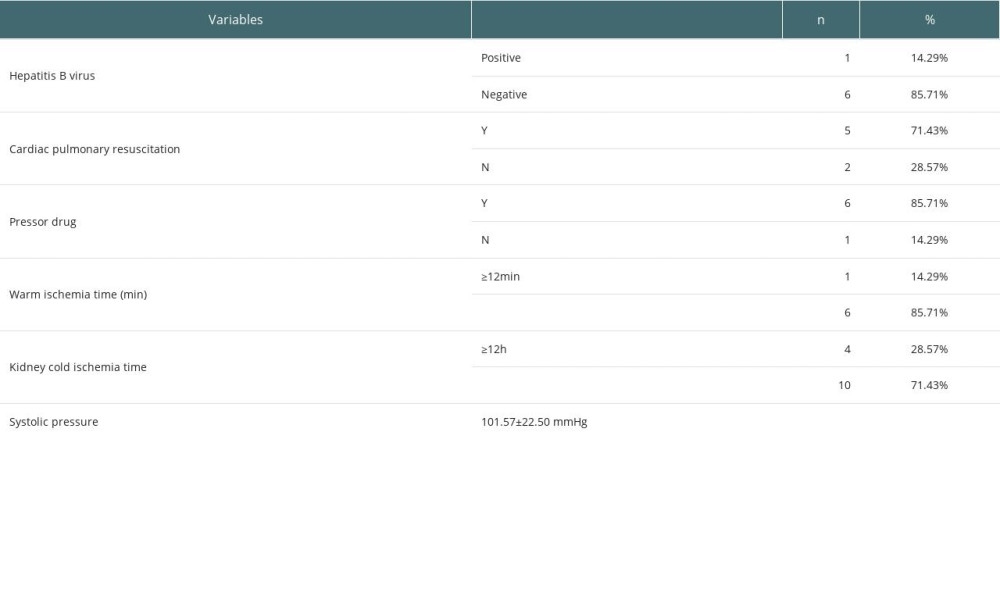 Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation.
Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation.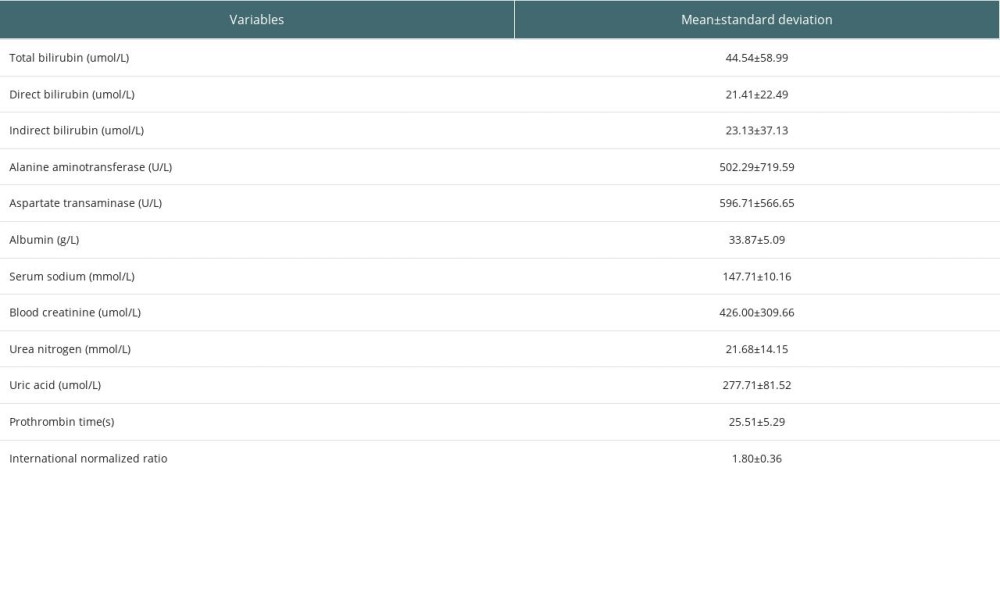 Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases.
Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases.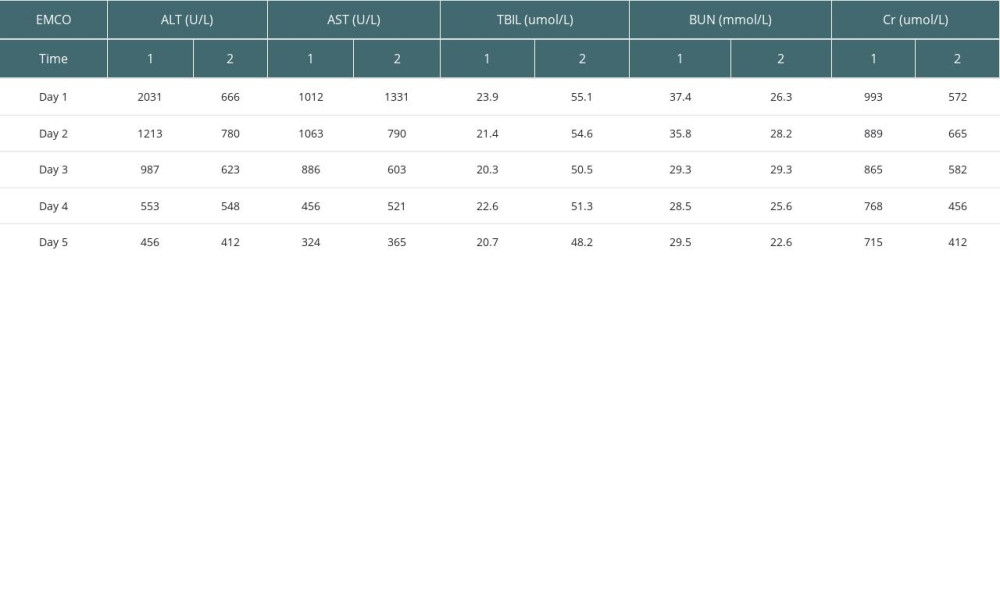 Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases.
Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases.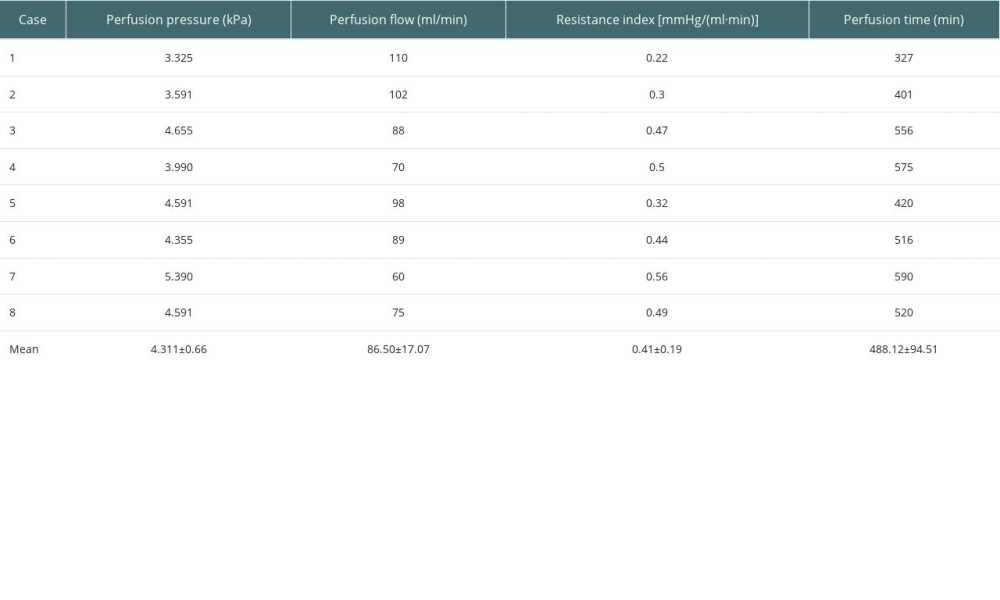 Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients.
Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients.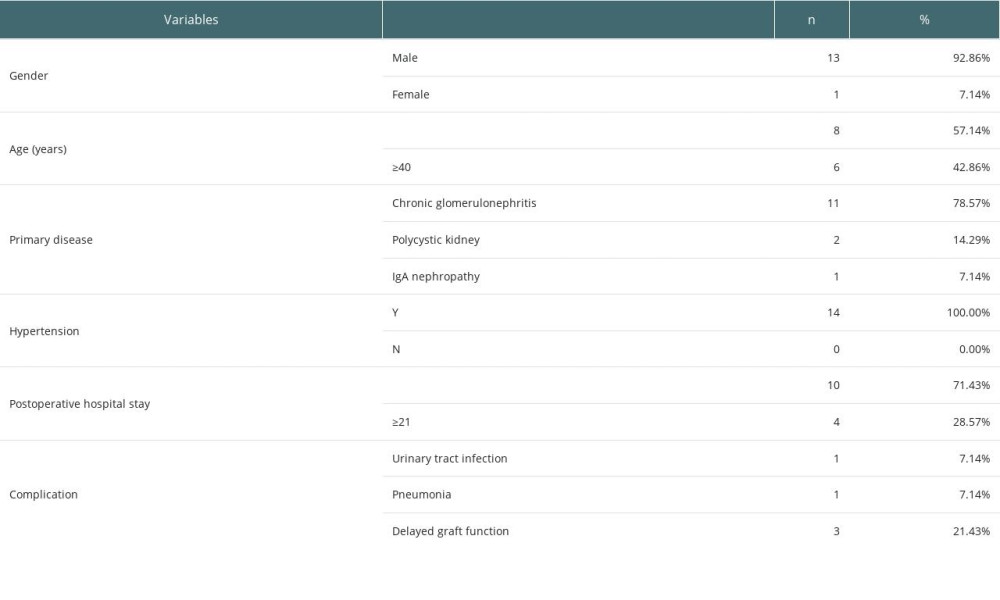 Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients.
Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients.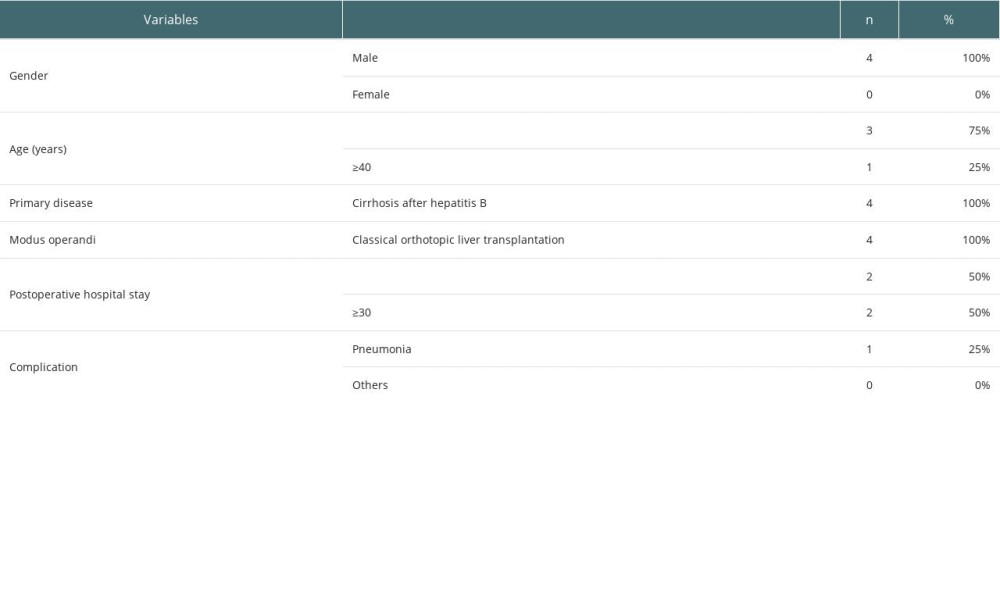 Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients.
Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients.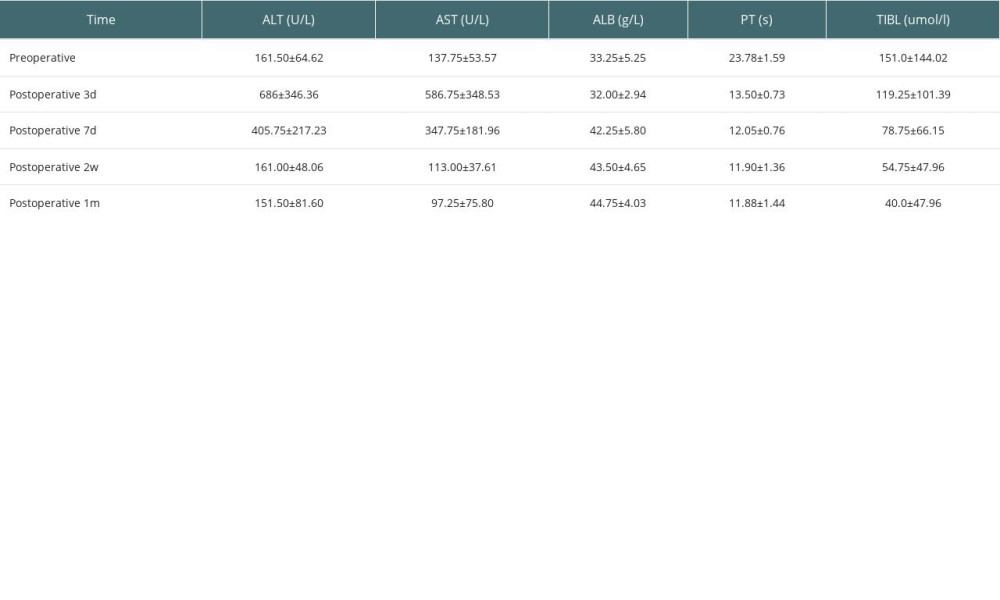
References
1. Snoeijs MG, Schaubel DE, Hené R, Kidneys from donors after cardiac death provide survival benefit: J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010; 21(6); 1015-21
2. Farney AC, Singh RP, Hines MH, Experience in renal and extrarenal transplantation with donation after cardiac death donors with selective use of extracorporeal support: J Am Coll Surg, 2008; 206(5); 1028-37
3. Aman S, Paul S, Chowdhury FR, Management of organophosphorus poisoning: Standard treatment and beyond: Crit Care Clin, 2021; 37(3); 673-86
4. Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Brooks DE: Clin Toxicol, 2015; 53(10); 962-1147
5. , China adult brain death judgment standards and operating specifications (Second Edition): Chinese Medical Journal, 2019; 99(17); 1288-32
6. Wu JH, Qiao PF, Sun XY, Evaluation and application of donors with primary central nervous system tumors: Clin Transplant, 2019; 33(10); e13677
7. Zhang F, Liao G, The effect of continuous hypothermic mechanical perfusion on the preservation of transplanted kidney and its research progress: Organ Transplantation, 2020; 11(4); 521-25
8. Lin X, Pathogenesis and treatment status of acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: Serpentine, 2020; 125(01); 117-19
9. Li X, Effect of Xuebijing injection on inflammatory mediators in patients with severe acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: Tianjin Pharmaceutical, 2010; 38(7); 593-95
10. Doi K, Rabb H, Impact of acute kidney injury on distant organ function: Recent findings and potential therapeutic targets: KidneyInt, 2016; 89(3); 555-64
11. , Anonymous technical operation specifications for cold preservation of cadaveric donor kidney by external mechanical perfusion (2019 Edition): Organ Transplant, 2019; 10(3); 263-66
12. Teixeira L, Henriques AC, Fonseca I, The effect of delayed graft function on graft and patient survival in kidney transplantation: An approach using competing events analysis: Transpl Int, 2015; 28(6); 738-50
Figures
 Figure 1. Pathological examination of donor kidney zero-point puncture biopsy. Figures A and B show the tubular type of epithelial cells in renal tubules. Some epithelial cells in renal tubules show edema with microvilli shedding (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×).
Figure 1. Pathological examination of donor kidney zero-point puncture biopsy. Figures A and B show the tubular type of epithelial cells in renal tubules. Some epithelial cells in renal tubules show edema with microvilli shedding (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×). Figure 2. Liver zero-point puncture for pathological examination. Figures A and B show hepatocytes with slight edema, slight gallbladder silt, small infiltration of inflammatory cells, and occasionally punctate necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×).
Figure 2. Liver zero-point puncture for pathological examination. Figures A and B show hepatocytes with slight edema, slight gallbladder silt, small infiltration of inflammatory cells, and occasionally punctate necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 40×). Figure 3. Comparison of creatinine before and after renal transplantation in 14 recipients.
Figure 3. Comparison of creatinine before and after renal transplantation in 14 recipients. Figure 4. Follow-up recipients/graft survival in liver transplant and kidney transplant.
Figure 4. Follow-up recipients/graft survival in liver transplant and kidney transplant. Tables
 Table 1. General information of donors.
Table 1. General information of donors. Table 2. Donor clinical parameters.
Table 2. Donor clinical parameters. Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation.
Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation. Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases.
Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases. Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases.
Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases. Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients.
Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients. Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients.
Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients. Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients.
Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients. Table 1. General information of donors.
Table 1. General information of donors. Table 2. Donor clinical parameters.
Table 2. Donor clinical parameters. Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation.
Table 3. Biochemical indicators before donor donation. Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases.
Table 4. The data of organ function maintained by ECMO in 2 cases. Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases.
Table 5. Data on LifePort perfusion in 8 donor kidney cases. Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients.
Table 6. Situation of renal transplant recipients. Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients.
Table 7. Situation of liver transplant recipients. Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients.
Table 8. Postoperative liver function index in 4 liver transplant recipients. In Press
18 Mar 2024 : Original article
Does Antibiotic Use Increase the Risk of Post-Transplantation Diabetes Mellitus? A Retrospective Study of R...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.943282
20 Mar 2024 : Original article
Transplant Nephrectomy: A Comparative Study of Timing and Techniques in a Single InstitutionAnn Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.942252
28 Mar 2024 : Original article
Association Between FEV₁ Decline Rate and Mortality in Long-Term Follow-Up of a 21-Patient Pilot Clinical T...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.942823
02 Apr 2024 : Original article
Liver Transplantation from Brain-Dead Donors with Hepatitis B or C in South Korea: A 2014-2020 Korean Organ...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.943588
Most Viewed Current Articles
05 Apr 2022 : Original article
Impact of Statins on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Living-Donor Liver TransplantationDOI :10.12659/AOT.935604
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e935604
12 Jan 2022 : Original article
Risk Factors for Developing BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of ...DOI :10.12659/AOT.934738
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e934738
22 Nov 2022 : Original article
Long-Term Effects of Everolimus-Facilitated Tacrolimus Reduction in Living-Donor Liver Transplant Recipient...DOI :10.12659/AOT.937988
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e937988
15 Mar 2022 : Case report
Combined Liver, Pancreas-Duodenum, and Kidney Transplantation for Patients with Hepatitis B Cirrhosis, Urem...DOI :10.12659/AOT.935860
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e935860








