18 December 2020: Original Paper
Usefulness of a Balloon Catheter for Intraoperative Cholangiography During Living Donor Hepatectomy: A Product Investigation
Katsunori Sakamoto1ABCDEF*, Kohei Ogawa1AB, Kei Tamura1BC, Miku Iwata1B, Akimasa Sakamoto1B, Takashi Matsui1B, Yusuke Nishi1B, Tomoyuki Nagaoka1B, Naotake Funamizu1B, Akihiro Takai1B, Yasutsugu Takada1ADOI: 10.12659/AOT.929062
Ann Transplant 2020; 25:e929062
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Intraoperative cholangiography (IOC) during living donor liver procurement for liver transplantation is an essential procedure to avoid biliary complications in the donor and to assess the details of the biliary anatomy of the graft liver for the recipient. There are limitations to IOC using conventional methods, including that the contrast medium often passes immediately to the duodenum, making continuous enhancement of the peripheral biliary tree difficult. The usefulness of a thin balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon for IOC was evaluated.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: A pediatric angiography balloon catheter was used for IOC.
RESULTS: The device was used in 2 living donors, and high-quality continuous images were easily achieved. There were no perioperative biliary complications in either donor.
CONCLUSIONS: A thin balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon catheter is useful in operations for both the donor and recipient because it allows more accurate division of the bile duct because of the clear IOC images.
Keywords: Cholangiography, Liver Transplantation, Living Donors, catheters, Hepatectomy, Liver
Background
Living donor liver transplants are relatively common in Japan due to the scarcity of deceased donors [1]. Intraoperative cholangiography (IOC) during living donor liver procurement for liver transplantation is an essential procedure to avoid biliary complications in the donor and to assess the details of the biliary anatomy of the graft liver for the recipient [2]. However, there are limitations to IOC using conventional methods, including that the contrast medium often passes immediately to the duodenum, making continuous enhancement of the peripheral biliary tree difficult. Therefore, we considered the use of a balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon to be the best device for use in IOC. A pediatric angiography catheter appears to be suitable, and its usefulness for IOC was evaluated.
Material and Methods
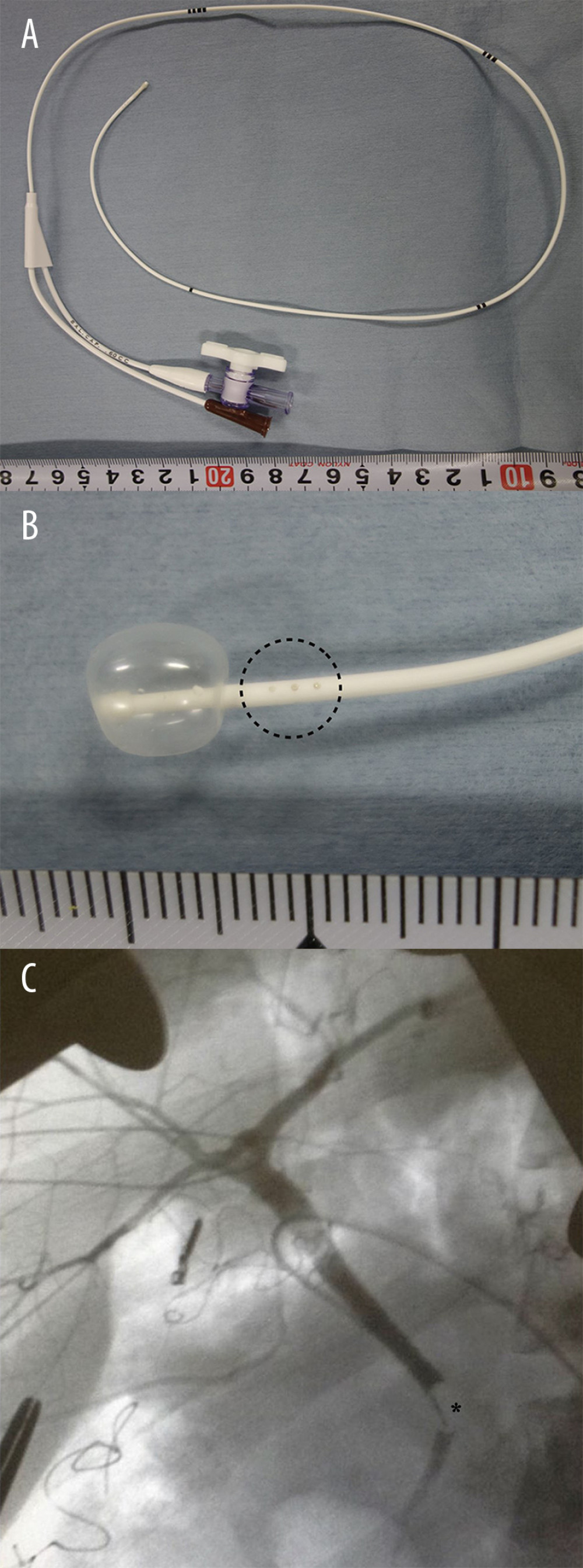
Conventionally, we use a 4-Fr Atom utility tube (Atom Medical Corp., Saitama, Japan) for IOC, which is a simple single-lumen catheter. On the other hand, a pediatric angiography catheter [Arrow Berman Angiographic Catheter, length 50 cm, external diameter 1.4 mm (4 Fr), Teleflex Incorporated, Wayne, PA, USA] (Figure 1A, 1B), which is a thin, radio-opaque, balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon, was evaluated for IOC.
In the procedure for IOC, the catheter was inserted from the cystic duct following cholecystectomy, and the tip of the catheter was placed in the common bile duct under radiographic guidance. IOC was performed after balloon dilation. The balloon catheter was also useful for the bile leak test after suturing of the stump of the remnant hepatic duct.
Results
This device was used in 2 living liver donors: 1 posterior sector graft donor and 1 right lobe graft donor. The insertion and positioning of the tip of the catheter were easily performed, and high-quality continuous images were achieved in both donors (Figure 1C). The hepatic duct for graft liver was divided appropriately in both donors. There were no perioperative biliary complications in either donor.
Discussion
The use of a conventional, simple, single-lumen catheter for IOC has a major limitation in that the contrast medium often passes immediately to the duodenum, and clear biliary tree images are difficult to obtain. Although clamping of the distal bile duct may resolve the issue, it is not always useful in all donors, such as in those with a low-confluence cystic duct. In addition, minimal dissection of the remnant bile duct is recommended for living donors to avoid biliary ischemia. The Trendelenburg position during IOC also does not always provide enough information. A balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon may be useful for IOC because it resolves all of the above problems.
Balloon catheter use for IOC for liver surgery or common bile duct exploration has been reported previously [3], but the reported smallest conventional size catheter was 6 Fr (external diameter 2 mm), which is too large to cannulate healthy donors whose cystic ducts are very thin. Actually, a 6-Fr IOC balloon catheter could not be cannulated to the cystic duct during donor operations in our experience.
The use of balloon catheters does, however, have some limitations. The catheter requires careful intraoperative positioning to avoid cystic duct or papilla of Vater injury secondary to balloon inflation. However, the pediatric angiography balloon catheter may also be useful in fluorescent cholangiography in which indocyanine green is injected into the cystic duct [4,5], since it may be retained in the bile duct when the balloon is inflated. Therefore, the balloon catheter may also be useful for laparoscopic donor hepatectomy in which the bile duct is often divided under fluorescent cholangiographic guidance [6]. Of course, it may also be useful for conventional liver and biliary surgery, not only for donor surgery, and it is expected to be made as a new low-cost device for IOC.
Conclusions
A thin balloon catheter with side holes located proximal to the balloon is useful in operations for both the donor and recipient because it allows more accurate division of the bile duct because of the clear IOC images.
References
1. Ogawa K, Takada Y: Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016; 1; 35
2. Nakamura T, Tanaka K, Kiuchi T, Anatomical variations and surgical strategies in right lobe living donor liver transplantation: Lessons from 120 cases: Transplantation, 2002; 73(12); 1896-903
3. Kubo S, Sakai K, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K, Intraoperative cholangiography using a balloon catheter in liver surgery: World J Surg, 1986; 10(5); 844-50
4. Ishizawa T, Saiura A, Kokudo N, Clinical application of indocyanine green-fluorescence imaging during hepatectomy: Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2016; 5(4); 322-28
5. Kawaguchi Y, Ishizawa T, Masuda K, Hepato-biliary surgery guided by a novel fluorescent imaging technique for visualizing hepatic arteries, bile ducts, and liver cancers on color images: J Am Coll Surg, 2011; 212; e33-39
6. Hasegawa Y, Nitta H, Takahara T, Pure laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy using the Glissonean pedicle approach (with video): Surg Endosc, 2019; 33(8); 2704-9
In Press
28 Mar 2024 : Original article
Association Between FEV₁ Decline Rate and Mortality in Long-Term Follow-Up of a 21-Patient Pilot Clinical T...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.942823
02 Apr 2024 : Original article
Liver Transplantation from Brain-Dead Donors with Hepatitis B or C in South Korea: A 2014-2020 Korean Organ...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.943588
02 Apr 2024 : Original article
Effect of Dexmedetomidine Combined with Remifentanil on Emergence Agitation During Awakening from Sevoflura...Ann Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.943281
03 Apr 2024 : Review article
Alternative Therapies in Transplantology as a Promising Perspective in MedicineAnn Transplant In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AOT.943387
Most Viewed Current Articles
05 Apr 2022 : Original article
Impact of Statins on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Living-Donor Liver TransplantationDOI :10.12659/AOT.935604
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e935604
12 Jan 2022 : Original article
Risk Factors for Developing BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of ...DOI :10.12659/AOT.934738
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e934738
22 Nov 2022 : Original article
Long-Term Effects of Everolimus-Facilitated Tacrolimus Reduction in Living-Donor Liver Transplant Recipient...DOI :10.12659/AOT.937988
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e937988
15 Mar 2022 : Case report
Combined Liver, Pancreas-Duodenum, and Kidney Transplantation for Patients with Hepatitis B Cirrhosis, Urem...DOI :10.12659/AOT.935860
Ann Transplant 2022; 27:e935860